QUANTUM MECHANICS (3H)
Quantum Chemistry Syllabus:
- 1. Quantum mechanics and its necessity,
- 2. experiments supporting quantization concept of electromagnetic radiation, blackbody radiation,
- 3. photoelectric effect,
- 4. Compton effect,
- 5. spectroscopic observations;
- 6. de Broglie’s wave particle dualism; matter waves;
- 7. double-slit experiment
- 8. Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle.
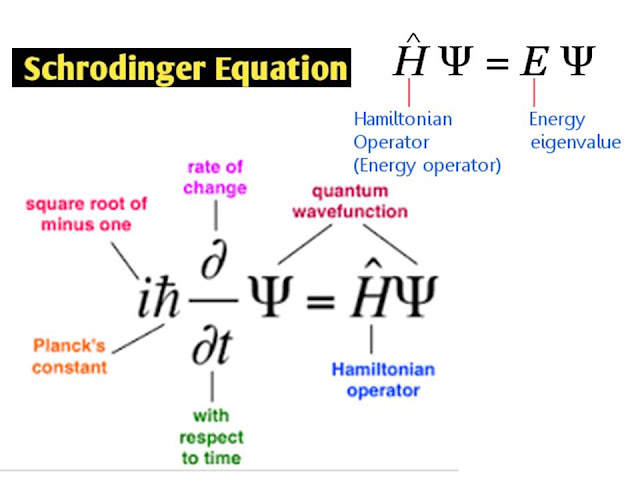
- 9. Dynamics of microcopic systems: Schrodinger’s wave equation, its deduction,
- 10. particle in a box problem: one and three dimensional boxes,
- 11. Eigen functions and Eigen values,
- 12. Schrodinger’s wave equation for H-atom,
- 13. separation of radial and angular functions,
- 14. solutions for wave functions,
- 15. derivation of different quantum numbers,
- 16. wave functions for different orbitals,
- 17. orbital shapes and orientations for H-like atom.
1. Quantum mechanics and its necessity (Overview):
- 2. experiments supporting quantization concept of electromagnetic radiation,
- blackbody radiation:
Numerical problem on Photoelectric effect
https://thefactfactor.com/facts/pure_science/physics/threshold-frequency/4877/
Compton effect:
- λi is initial wavelength, λf is the wavelength after scattering, m0 is the electron rest mass, c is the speed of light, and θ is the scattering angle.
- Compton scattering was discovered by Arthur Holly Compton.
- Compton scattering is the scattering of a photon by a charged particle, usually an electron.
- It results in a decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of the photon (which may be an X-ray or gamma ray photon), called the Compton effect.
- Part of the energy of the photon is transferred to the recoiling electron.
- Inverse Compton scattering occurs when a charged particle transfers part of its energy to a photon.
de-Broglie equation

- The
universe
on the smallest scale is “quantised”
– matter and energy exist in tiny “packets”
photons of energy and fundamental
particles of matter.
-Matter and energy have a wave- particle duality.
- Prince Louis Victor de Broglie (pronounced de-broy) put together the ideas of Planck
and Einstein and formulated a relationship between wavelength and momentum of
both waves and particles.
Significance of de Broglie's hypothesis

......................................................................................................................................






















































No comments:
Post a Comment